MySQL
Overview
MySQL is an open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) from Oracle that uses Structured Query Language (SQL) for database access and management. Qarbine uses the mysql node.js driver for interacting with the MySQL database.
Some independent databases, such as Singlestore, CockroachDB, and Yugabyte also use the MySQL wire protocol.
MySQL Configuration Information
You likely already have an application and tools configured to access MySQL. Determine your MySQL endpoint which includes
- URL,
- port number (the default is 3306),
- account name, and
- account password.
Many cloud services have options limiting the IP addresses which can connect to services. Verify the Qarbine host has access to the MySQL endpoint. A check for this is also part of the instructions below.
Qarbine Configuration
Compute Node Preparation
Determine which compute node service endpoint you want to run this data access from. That URL will go into the Data Service’s Compute URL field. Its form is “https://domain:port/dispatch”. A sample is shown below.
The port number corresponds to a named service endpoint configured on the given target host. For example, the primary compute node usually is set to have a ‘main’ service. That service’s configuration is defined in the ˜./qarbine.service/config/service.main.json file. Inside that file the following driver entry is required when using the MySQL interaction.
"drivers" :[
. . .
"./driver/mySqlDriver.js"
]
The relevant configuration file name for non primary (main) Qarbine compute nodes is service.NAME.json. Remember to have well formed JSON syntax or a startup error is likely to occur. If you end up adding that entry then restart the service via the general command line syntax
pm2 restart <service>
For example,
pm2 restart main
or simply
pm2 restart all
Data Service Definition
Open the Administration Tool.
Navigate to the Data Services tab.
A data service defines on what compute node a query will run by default along with the means to reach to target data. The latter includes which native driver to use along with settings corresponding to that driver. Multiple Data Sources can reference a single Data Service. The details of any one Data Service are thus maintained in one spot and not spread out all over the place in each Data Source. The latter is a maintenance and support nightmare.
To begin adding a data service click
On the right hand side enter a name and optionally a description.
Set the Compute URL field based on the identified compute node above. Its form is “https://domain:port/dispatch”. A sample is shown below.
Choose the driver and set the values as shown below.
Enter the values for the URL, account information, and database into the fields shown below.

You can reference environment variables using the syntax %NAME%. Any strings should be quoted and the key\value pairs separated by commas.
Test your settings by clicking on the toolbar image highlighted below.
The results vary depending on the actual server being access. The result should be something similar to the following
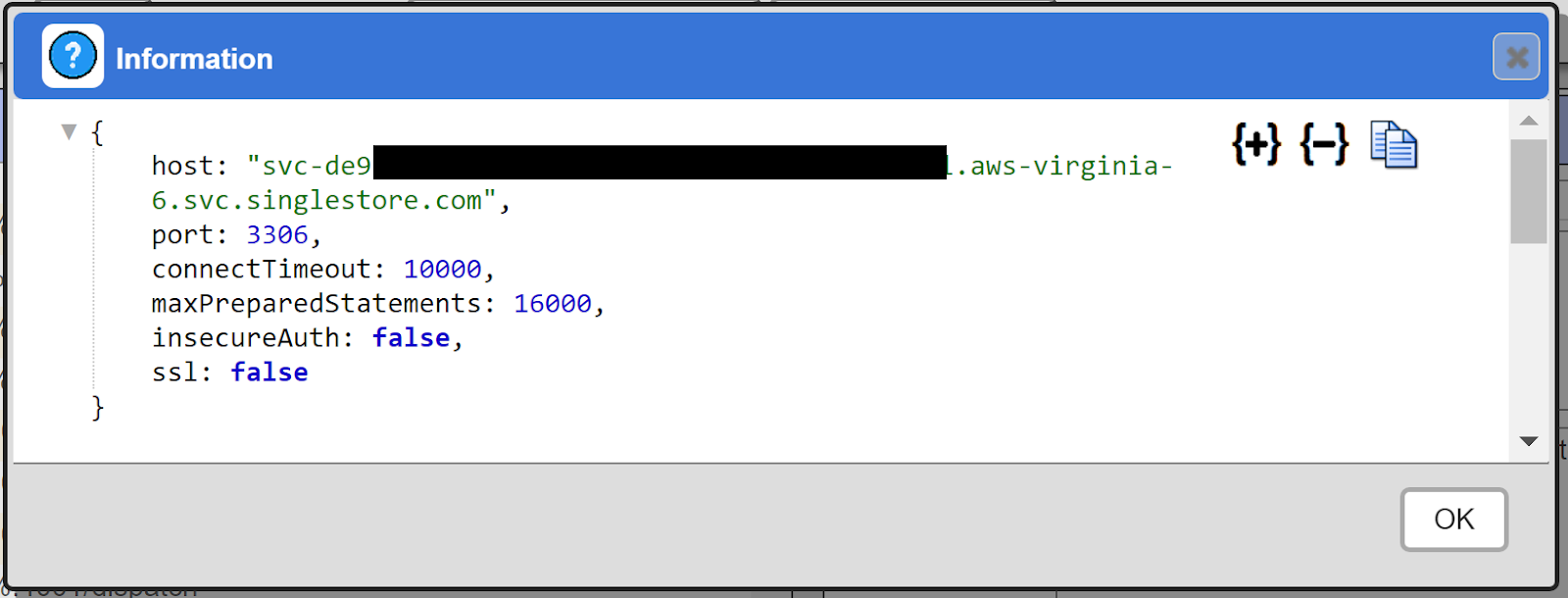
Save the Data Service by clicking on the image highlighted below.
The data service will be known at the next log on time.